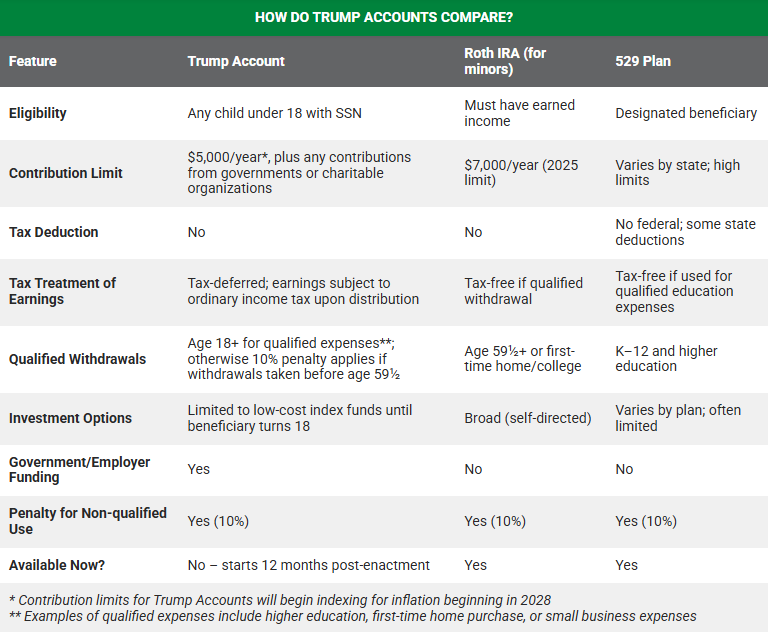
Why Trump Accounts Could Completely Upset the Retirement Game—And What It Means for Your IRA Savings.
However, the management of these new accounts, their still unclear tax status, and their restricted investment framework (Index funds only) make them a tool to be used with discernment, as a complement to, not a replacement for, existing retirement savings instruments.
IRAs FAQs
An IRA (Individual Retirement Account) allows you to make tax-deferred investments to save money and provide financial security when you retire. There are different types of IRAs, the most common being a traditional one – in which contributions may be tax-deductible – and a Roth IRA, a personal savings plan where contributions are not tax deductible but earnings and withdrawals may be tax-free. When you add money to your IRA, this can be invested in a wide range of financial products, usually a portfolio based on bonds, stocks and mutual funds.
Yes. For conventional IRAs, one can get exposure to Gold by investing in Gold-focused securities, such as ETFs. In the case of a self-directed IRA (SDIRA), which offers the possibility of investing in alternative assets, Gold and precious metals are available. In such cases, the investment is based on holding physical Gold (or any other precious metals like Silver, Platinum or Palladium). When investing in a Gold IRA, you don’t keep the physical metal, but a custodian entity does.
They are different products, both designed to help individuals save for retirement. The 401(k) is sponsored by employers and is built by deducting contributions directly from the paycheck, which are usually matched by the employer. Decisions on investment are very limited. An IRA, meanwhile, is a plan that an individual opens with a financial institution and offers more investment options. Both systems are quite similar in terms of taxation as contributions are either made pre-tax or are tax-deductible. You don’t have to choose one or the other: even if you have a 401(k) plan, you may be able to put extra money aside in an IRA
The US Internal Revenue Service (IRS) doesn’t specifically give any requirements regarding minimum contributions to start and deposit in an IRA (it does, however, for conversions and withdrawals). Still, some brokers may require a minimum amount depending on the funds you would like to invest in. On the other hand, the IRS establishes a maximum amount that an individual can contribute to their IRA each year.
Investment volatility is an inherent risk to any portfolio, including an IRA. The more traditional IRAs – based on a portfolio made of stocks, bonds, or mutual funds – is subject to market fluctuations and can lead to potential losses over time. Having said that, IRAs are long-term investments (even over decades), and markets tend to rise beyond short-term corrections. Still, every investor should consider their risk tolerance and choose a portfolio that suits it. Stocks tend to be more volatile than bonds, and assets available in certain self-directed IRAs, such as precious metals or cryptocurrencies, can face extremely high volatility. Diversifying your IRA investments across asset classes, sectors and geographic regions is one way to protect it against market fluctuations that could threaten its health.









Post Comment